Spring |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › predestroy spring不触发 › Spring |
Spring
|
@[toc]
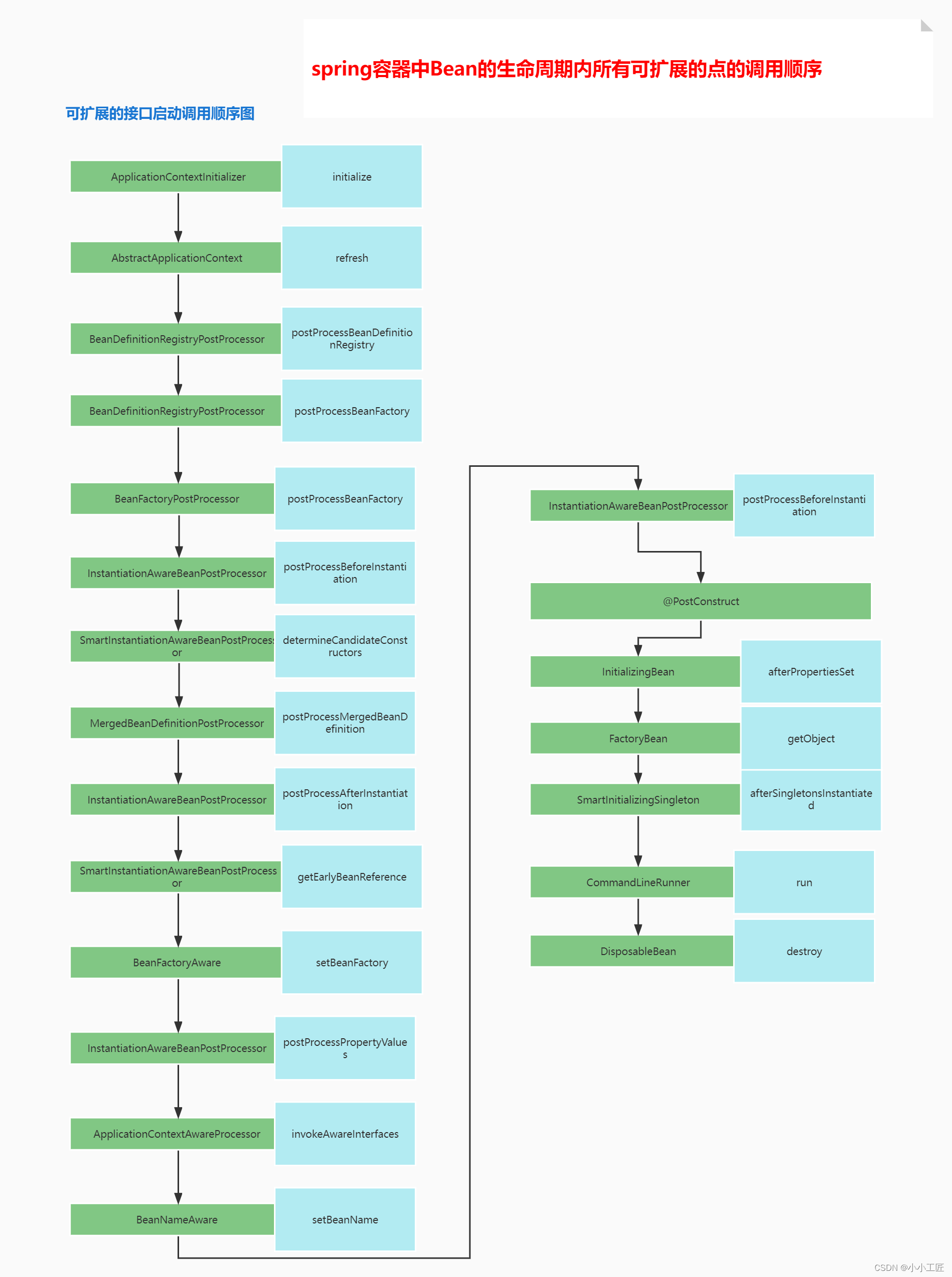
Spring Boot - 扩展接口一览
严格意义上来说这个并不算一个扩展点,其实就是一个标注。 其作用是在bean的初始化阶段,如果对一个方法标注了@PostConstruct,会先调用这个方法。 触发时机是在postProcessBeforeInitialization之后InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet之前。 源码解析带着这个疑问: 为什么@PostConstruct注解的方法会在程序启动的时候执行? 源码面前,了无秘密。 结合对Spring生命周期的理解, bean的创建过程,我们可以推测@PostConstruct方法将在最后生成Bean的时候被调用。 org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors() BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#getBean org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean
我们从 AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean 开始看 protected T doGetBean( String name, @Nullable Class requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); Object bean; Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { // ... } else { try { // ... // 单例 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> { try { // 创建Bean的实例 return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // ... } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // ... } else { // ... } } catch (BeansException ex) { cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); throw ex; } } // ... return (T) bean; }createBean包含了创建一个Bean的核心逻辑,继续跟进createBean方法 @Override protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { try { // 委托给了doCreateBean处理 Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args); // ... return beanInstance; } catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) { // ... } catch (Throwable ex) { // ... } }继续 doCreateBean protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; // ... // 创建Bean的实例对象 if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } // ... // 初始化一个Bean Object exposedObject = bean; try { // 处理Bean的注入 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); // 处理Bean的初始化操作 exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { // ... } // ... return exposedObject; }BeanFactory的getBean()方法将会去创建Bean,在doCreateBean方法的创建逻辑中主要包含了三个核心逻辑: 1)创建一个Bean的实例对象,createBeanInstance方法执行2)处理Bean之间的依赖注入,比如@Autowired注解注入的Bean。populateBean方法将会先去处理注入的Bean,因此对于相互注入的Bean来说不用担心Bean的生成先后顺序问题。3)Bean实例生成,相互注入以后。还需要对Bean进行一些初始化操作。比如@PostConstruct注解注释的方法,将再初始化的时候被解析并调用。当然还有一些Aware接口,@Schedule注解啥的也会做相应的处理。
继续跟进初始化过程,进入initializeBean方法 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { // ... Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { // 初始化前置处理 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { // 调用初始化方法 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { // ... } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { // 初始化后置处理 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }主要包含了初始化的前置、后置处理,以后初始化方法的调用。@PostConstruct注解将在applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization这个前置处理
继续 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization前置方法 @Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result; }遍历了在spring启动过程中被注册的BeanPostProcessor接口,并调用其前置方法。 BeanPostProcessor后置处理器接口,当一个Bean生成以后,会针对生成的Bean做一些处理。 比如注解了@PostConstruct注解的Bean将会被其中一个BeanPostProcessor处理。或者一些@Schedule之类注解的Bean也会被处理,等一些所谓的后置处理操作。
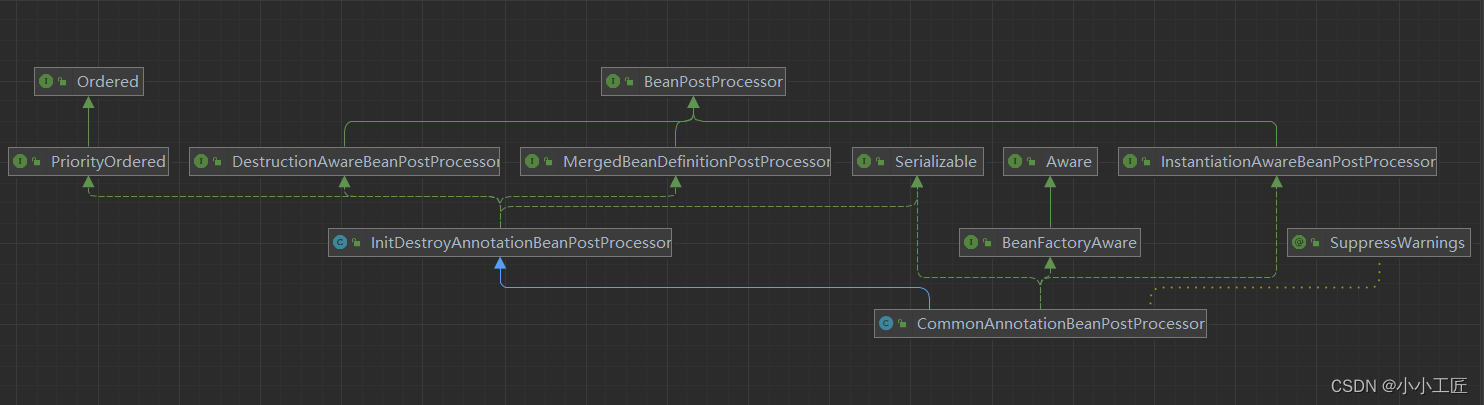
@PostConstruct注解是会被一个专门的BeanPostProcessor接口的具体实现类来处理的 InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
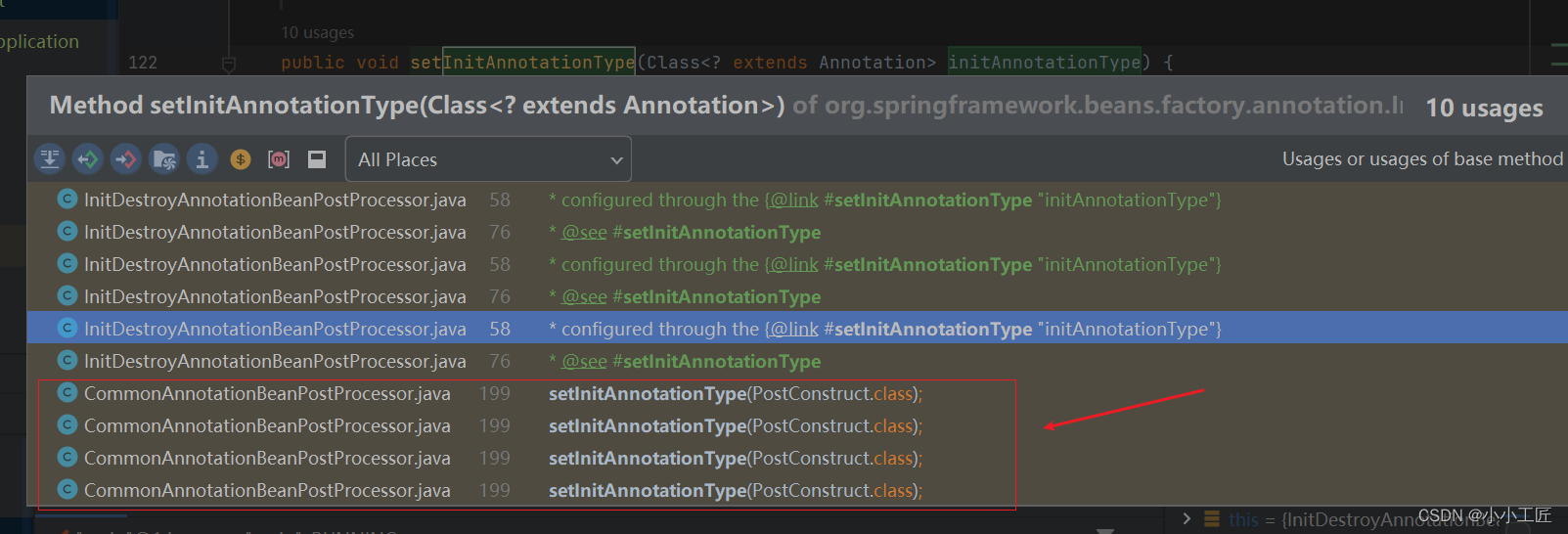
进入到进InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeanInitialization方法 @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // 元数据解析 LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass()); try { // 触发初始化方法 metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException()); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex); } return bean; }findLifecycleMetadata方法将会解析元数据,@PostConstruct注解的初始化方法也会在这里被找到。invokeInitMethods方法将会触发上一步被找到的方法。猜测的话通过反射将Method给找出来,然后再通过反射去调用这些method方法,那我们去验证下 private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class clazz) { // ... LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) { metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { // 构建元数据 metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata); } return metadata; } } return metadata; }如上是双重校验来控制缓存,重点看buildLifecycleMetadata这个构建方法即可 private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class clazz) { List initMethods = new ArrayList(); Class targetClass = clazz; do { final List currInitMethods = new ArrayList();// 变量类中的方法Method对象 ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> { // 判断是否被@PostConstruct注解注释 if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) { LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method); currInitMethods.add(element); } // ... }); // 添加到集合中,后续调用 initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods); // ... targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass(); } while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class); return new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods); }这里包含了currInitMethods 和 currDestroyMethods 方法 doWithLocalMethods这个工具方法将会从class中获取方法的反射对象。而后判断该方法是否被被initAnnotationType指定的注释注解。最后,添加到initMethods集合当中供后续反射调用。这里还向父类进行了递归处理,直到Object类为止。 看看 initAnnotationType
@PostConstruct注解被设置为了initAnnotationType的值。值得注意的是,这是在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这个后置处理器的构造方法中执行的。
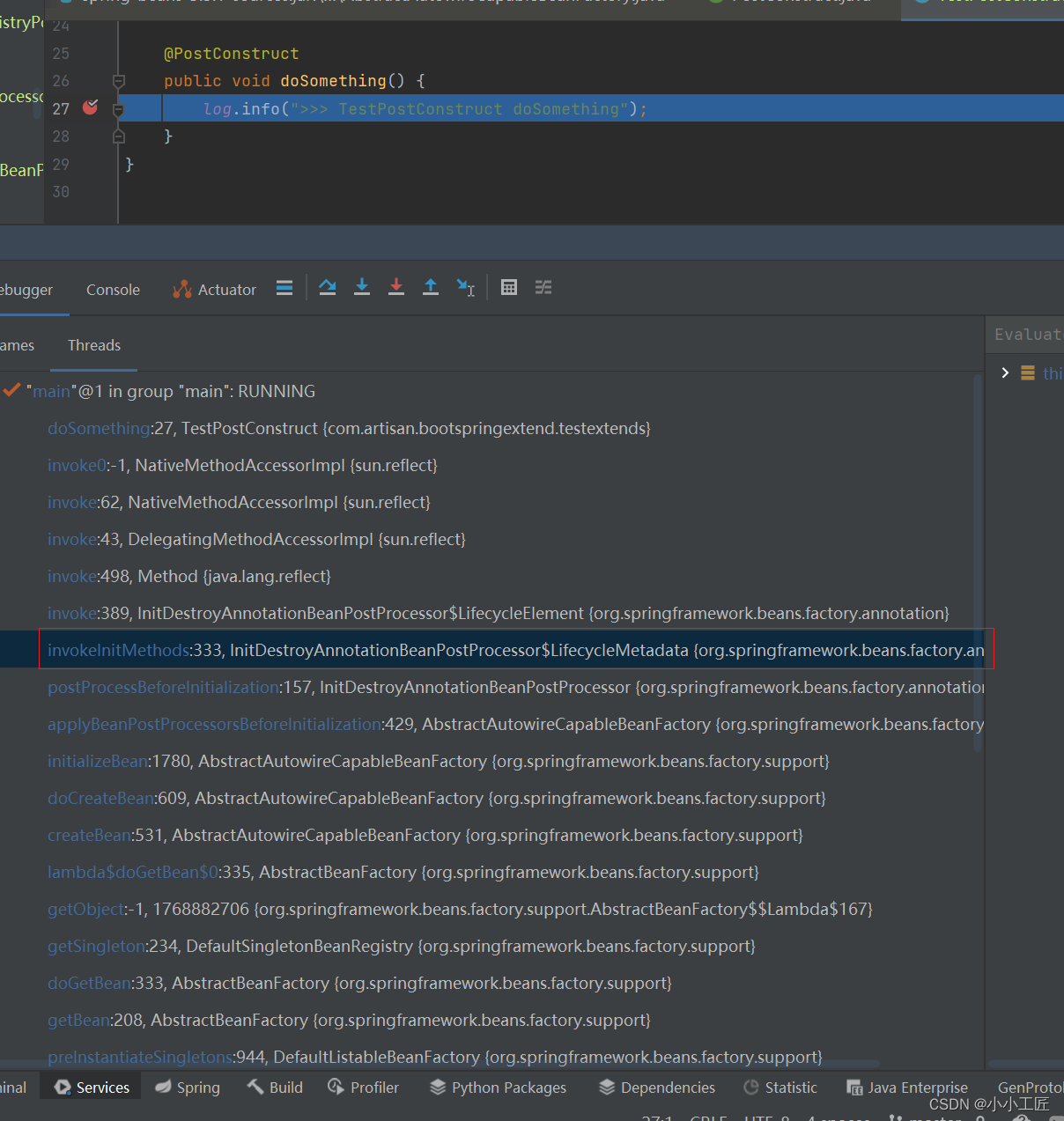
我们可以看到解析过程是通过反射来获取@PostConstruct注解的方法,并放到一个List集合里面去。 那继续看看这些Method被调用的过程吧。 回到InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization方法 @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass()); try { metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException()); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex); } return bean; }继续 invokeInitMethods方法 public void invokeInitMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable { Collection checkedInitMethods = this.checkedInitMethods; Collection initMethodsToIterate = (checkedInitMethods != null ? checkedInitMethods : this.initMethods); if (!initMethodsToIterate.isEmpty()) { for (LifecycleElement element : initMethodsToIterate) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Invoking init method on bean '" + beanName + "': " + element.getMethod()); } // 调用 element.invoke(target); } } }继续 public void invoke(Object target) throws Throwable { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.method); this.method.invoke(target, (Object[]) null); }继续跟 就已经到JDK了 @CallerSensitive public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException { if (!override) { if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) { Class caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers); } } MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile if (ma == null) { ma = acquireMethodAccessor(); } return ma.invoke(obj, args); }小结一下: spring的Bean在创建的时候会进行初始化,而初始化过程会解析出@PostConstruct注解的方法,并反射调用该方法。
输出结果 2022-12-04 22:48:57.994 INFO 30472 --- [ main] c.a.b.testextends.TestPostConstruct : >>> TestPostConstruct no arg cons called 2022-12-04 22:55:00.920 INFO 30472 --- [ main] c.a.b.testextends.TestPostConstruct : >>> TestPostConstruct doSomething
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |